Accessibility Features: Streaming Media Players and Inclusive Design Trends
Streaming media players are transforming digital accessibility by incorporating inclusive design fea…….

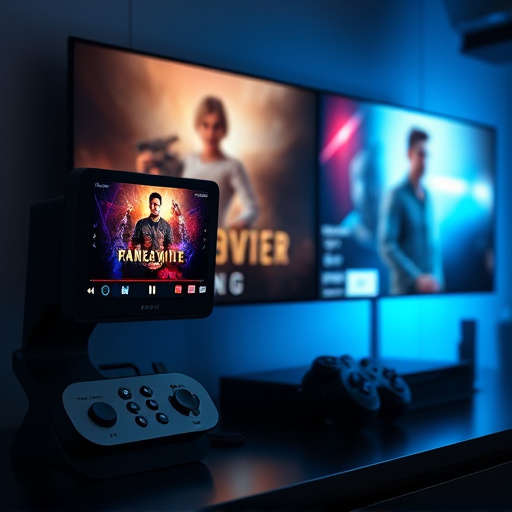
Streaming media players are transforming digital accessibility by incorporating inclusive design features that benefit users with visual or auditory impairments. Key aspects include text-to-speech functionality, synchronized captions, adjustable display settings, and closed captions. These innovations ensure everyone can access and enjoy multimedia content seamlessly, fostering a more accessible and engaging digital landscape. With ongoing advancements in AI, automatic captioning and personalized settings will further enhance the user experience for all.
Accessibility features are transforming digital interactions, ensuring inclusivity for all users. This article delves into the foundational principles of accessible design, exploring how streaming media players play a pivotal role in enhancing user experiences. From visual and auditory accommodations to future trends in accessible media technologies, we navigate the dynamic landscape of accessibility. Understanding these aspects is crucial for creating inclusive digital environments, catering to diverse needs with innovative solutions.
- Understanding Accessibility Features: A Foundation for Inclusive Design
- Streaming Media Players and Their Role in Enhancing Accessibility
- Implementing Visual and Auditory Accommodations: Best Practices
- Future Trends: Accessible Media Technologies Shaping the Digital Landscape
Understanding Accessibility Features: A Foundation for Inclusive Design

Accessibility features are a fundamental aspect of inclusive design, ensuring that digital content and applications can be used by all individuals, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. By implementing these features, designers create an environment where everyone can engage with technology seamlessly. One key area is making streaming media players accessible, enabling users with visual impairments to enjoy video content through screen readers and text-to-speech functionality.
Understanding accessibility as a design foundation involves recognizing diverse user needs. It encourages developers and designers to think beyond basic functionality and consider how their products can accommodate different learning styles, cognitive abilities, and physical disabilities. This inclusive approach not only benefits individuals with disabilities but also enhances the overall user experience for everyone, fostering a more accessible and engaging digital landscape.
Streaming Media Players and Their Role in Enhancing Accessibility

Streaming media players have become indispensable tools for enhancing accessibility, especially in the digital age. These devices are designed to make content consumption more inclusive by offering a range of features that cater to users with different needs and abilities. From adjusting audio settings for the hearing impaired to providing closed captions and voice control options, streaming media players play a pivotal role in ensuring everyone can access and enjoy multimedia content seamlessly.
In terms of accessibility, these players often include features like text-to-speech functionality, which assists visually impaired users by converting written content into spoken words. They also support high-definition video streaming with improved color contrast settings, aiding those with visual impairments. Moreover, the ability to customize interface layouts and use alternative input methods makes them versatile tools for a diverse user base. This not only enhances user experience but also promotes digital inclusion for all.
Implementing Visual and Auditory Accommodations: Best Practices

Implementing visual and auditory accommodations is a critical aspect of ensuring accessibility for all users, especially those with visual or hearing impairments. Best practices involve utilizing features built into streaming media players to enhance content delivery. For visual impairments, descriptions and captions should be standardized and synchronized with video content, allowing users to follow along seamlessly. This can be achieved by providing detailed scripts or using automated tools that generate captions in real-time.
Additionally, offering adjustable settings for display contrast, font sizes, and color schemes enables users to customize their viewing experience. For auditory impairments, streaming media players should support closed captions and alternative audio tracks. These features not only cater to different learning styles but also provide a more inclusive environment, ensuring everyone can access and enjoy the content equally.
Future Trends: Accessible Media Technologies Shaping the Digital Landscape

The future of digital accessibility is poised for significant advancements, and one prominent area of focus is accessible media technologies. As streaming media continues to dominate the entertainment and information landscape, developers are leveraging innovative tools and features within streaming media players to create more inclusive experiences. Voice control, text-to-speech functionality, and adjustable subtitles are becoming ubiquitous, ensuring that content is accessible to a broader audience, including those with visual or auditory impairments.
These trends signal a shift towards a more inclusive digital realm where accessibility is not merely an afterthought but an integral part of design. With advancements in artificial intelligence, we can expect even smarter features like automatic captioning and personalized settings tailored to individual users’ needs. This evolution not only broadens access to information but also enhances the overall user experience for everyone, fostering a more connected and inclusive online community.
In conclusion, understanding and implementing accessibility features is no longer a choice but an imperative for inclusive design. Streaming media players play a pivotal role in enhancing access to content, especially with evolving technologies. By embracing best practices for visual and auditory accommodations, creators can ensure their digital offerings are accessible to all. As we look ahead, future trends in accessible media technologies promise to further revolutionize the digital landscape, fostering an inclusive environment for everyone.